In this blog post, we will walk through the steps to configure Kubernetes Ingress on AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service). Ingress is an API object that manages external access to services within a Kubernetes cluster. We will be using the Nginx Ingress Controller for this demonstration
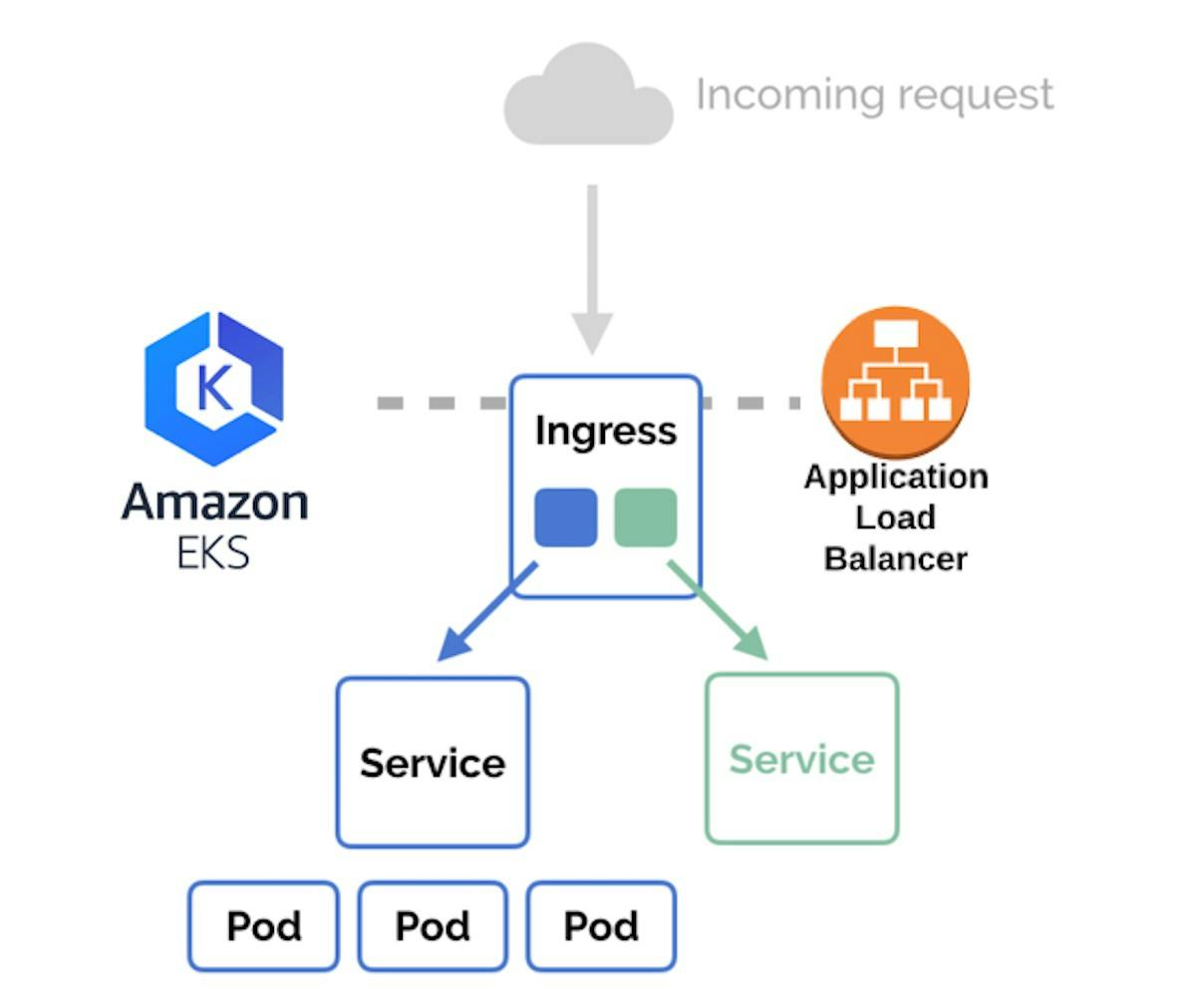
Kubernetes Ingress is a powerful tool for managing external access to services within a Kubernetes cluster. In this tutorial, we will walk through the process of setting up Kubernetes Ingress on an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) cluster. We will create and configure an Ingress Controller, deploy two sample applications, and configure path-based routing using Ingress resources.
To clone the content of the repository "https://github.com/BalajiiBharath/kubernetes-ingress.git" for your blog, you can follow these steps:
- Run the following command to clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/BalajiiBharath/kubernetes-ingress.git

Step 1: Configure Ingress Controller
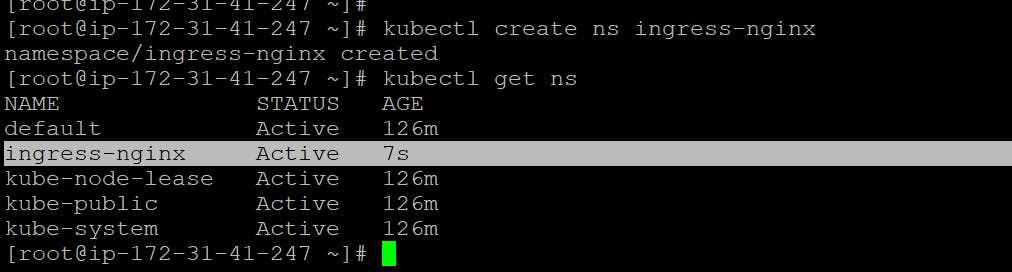
- Create a namespace for the Ingress Controller:
kubectl create ns ingress-nginx
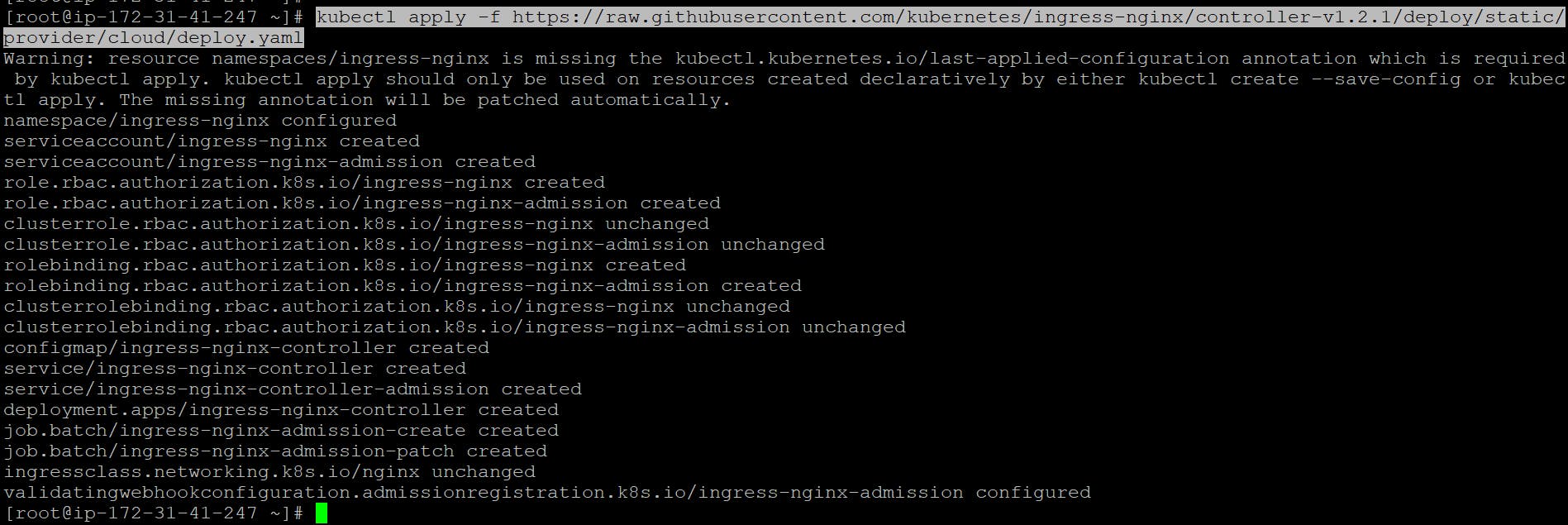
2. Deploy the Ingress Controller using the provided YAML file:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.2.1/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yaml
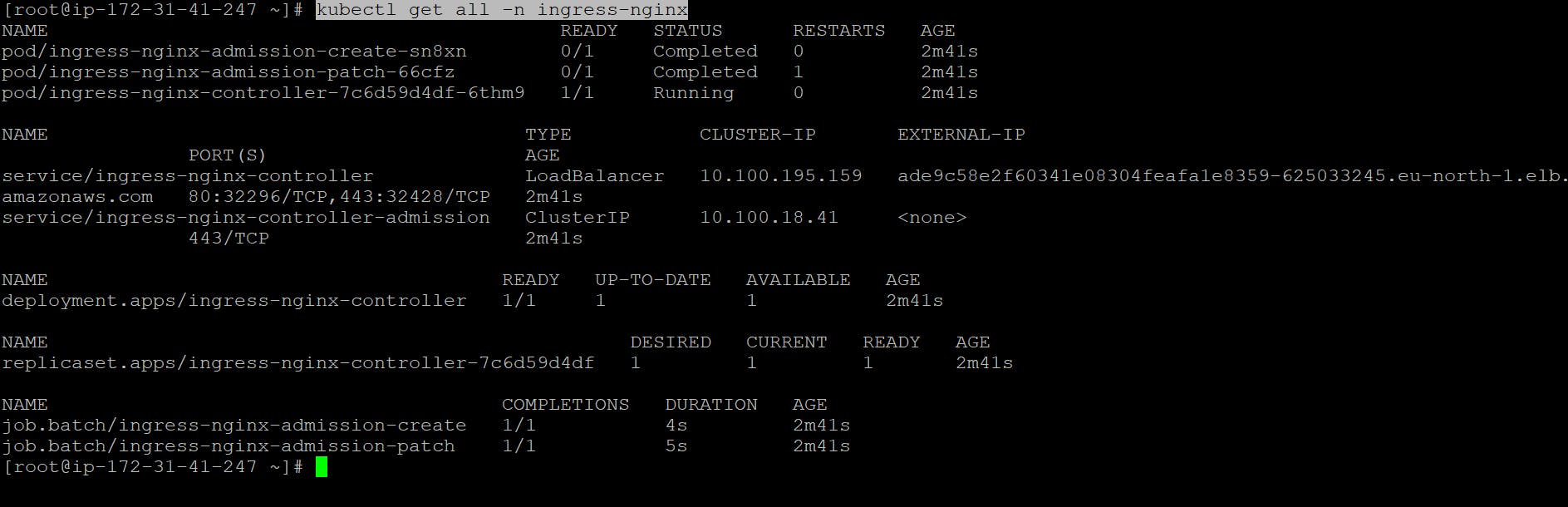
To check all the Ingress Controller resources using the kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx command, you can include the following content
kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx
Step 2: Deploy Sample Applications
Deploy the Nginx Application
Next, we will deploy two example services to test the Ingress functionality. We will deploy an Nginx service and an Apache service.
Create a file named onedeploy.yml and add the following YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 env: - name: TITLE value: "NGINX APP1" --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx spec: type: ClusterIP ports: - port: 80 selector: app: nginx
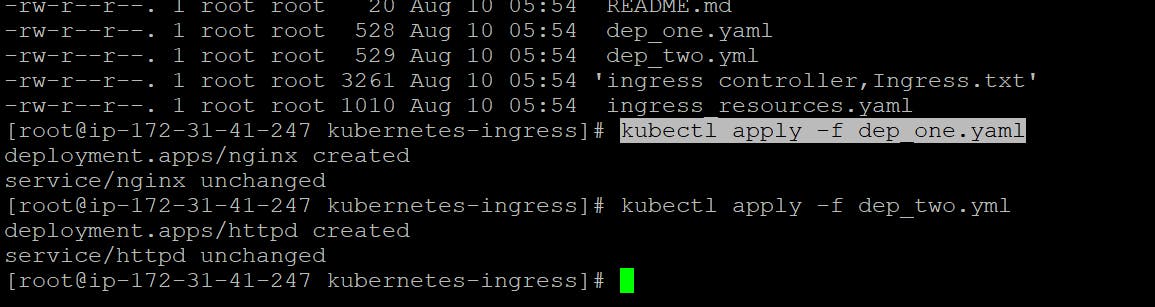
Apply the deployment using the following command:
kubectl apply -f onedeploy.yml
Deploy the Apache Httpd Application
Repeat the same steps for the Apache service by creating a file named twodeploy.yml with the following YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: httpd
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpd
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: httpd
spec:
containers:
- name: httpd
image: httpd
ports:
- containerPort: 80
env:
- name: TITLE
value: "APACHE APP2"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: httpd
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: httpd
Apply the deployment using the following command:
kubectl apply -f twodeploy.yml
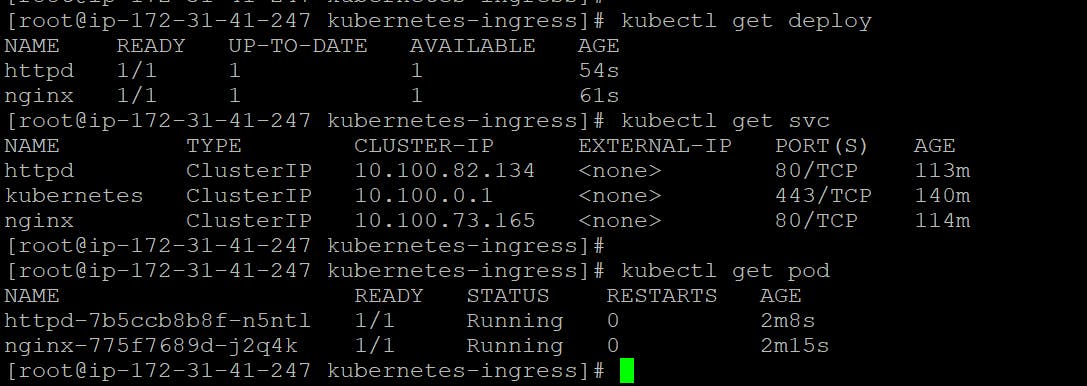
To verify that the deployments and services are running, use the following commands:
kubectl get deploy
kubectl get svc
kubectl get pods
Step 3: Configure Path-Based Routing with Ingress
Now, we will deploy the Ingress resource to route traffic to the respective services.
Create a file named ingress-resource.yml and add the following YAML:Now, we will deploy the Ingress resource to route traffic to the respective services.
Create a file named ingress-resource.yml and add the following YAML:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: k8s-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /nginx(/|$)(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
- path: /httpd(/|$)(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: httpd
port:
number: 80
- path: /(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
Apply the Ingress using the following command:
kubectl apply -f ingress-resource.yml

Step 4: Verify and Access the Ingress
To check the status of the Ingress, use the following command:
kubectl get ingAfter a few minutes, the Ingress will be provisioned, and you will see an address associated with it.
To access the services through the Ingress, use the load balancer DNS name provided by your cloud provider.

To check all the Ingress controller resources for the ingress-nginx namespace and display the output in the form of a table, you can use the following command:
kubectl get service ingress-nginx
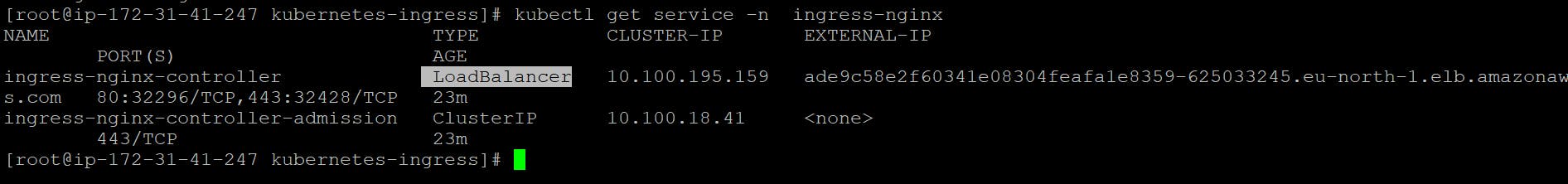
This command will list all the Ingress resources and Services in the ingress-nginx namespace. The output will include information such as the name, namespace, and other details of each resource.
Access the Nginx application:
http://<Ingress_IP_or_DNS>/nginx

Access the Apache Httpd application:
http://<Ingress_IP_or_DNS>/httpd
Congratulations! You have successfully configured Kubernetes Ingress on AWS EKS. Ingress allows you to route traffic to different services based on the defined rules. This provides a flexible and scalable way to expose your applications to the outside world.
Certainly, here are the steps to delete all the resources you've created based on the previous steps:
Step 1: Delete Ingress Controller and Namespace
Delete the Ingress Controller deployment:
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.2.1/deploy/static/provider/cloud/deploy.yamlDelete the Ingress Controller namespace:
kubectl delete ns ingress-nginx
Step 2: Delete Sample Applications
Delete the Nginx deployment and service:
kubectl delete -f onedeploy.ymlDelete the Apache Httpd deployment and service:
kubectl delete -f twodeploy.yml
Step 3: Delete Ingress Resource
Delete the Ingress resource:
kubectl delete -f ingress-resource.yml
By following these steps, you will remove all the resources you previously created. Please be cautious while performing deletions to avoid accidental loss of important data